The evolution of stereolithography technology has reached a pivotal moment with the introduction of advanced display systems that redefine precision manufacturing. Modern 3D printing services now demand equipment capable of delivering exceptional detail while maintaining production efficiency, creating new opportunities for industries requiring micro-level accuracy. The integration of sophisticated optical systems with refined mechanical components has enabled manufacturers to achieve previously unattainable levels of surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This technological advancement represents more than incremental improvement; it signifies a fundamental shift in how precision parts are conceptualized and produced across multiple industrial sectors.
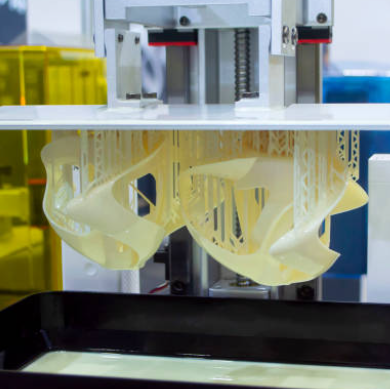
Revolutionary Display Technology in Modern Stereolithography
Advanced Optical Engineering for Enhanced Resolution
Contemporary stereolithography systems incorporate cutting-edge display technologies that utilize high-resolution LCD panels optimized for ultraviolet light transmission. These displays feature pixel densities exceeding traditional systems by significant margins, enabling the production of features with tolerances previously achievable only through traditional machining processes. The optical clarity and uniform light distribution characteristics ensure consistent polymerization across the entire build platform, eliminating the layer inconsistencies that plagued earlier generation systems. Advanced anti-aliasing algorithms work in conjunction with these displays to smooth edges and reduce the stair-stepping effects common in layer-based manufacturing processes.
The engineering behind these display systems involves sophisticated light management techniques that optimize photon delivery to the resin interface. Specialized coatings and optical filters ensure that only the appropriate wavelengths reach the photopolymer, maximizing cure efficiency while minimizing unwanted crosslinking in adjacent areas. This precise control over light exposure enables manufacturers to achieve surface finishes approaching injection-molded quality directly from the printer, significantly reducing post-processing requirements. The thermal management systems integrated within these displays maintain consistent operating temperatures, ensuring dimensional stability throughout extended production runs.
Mechanical Integration and Force Reduction Systems
The mechanical design of modern stereolithography systems emphasizes force reduction during the separation process, a critical factor in maintaining part integrity and surface quality. Traditional peeling forces often caused deformation or failure in delicate features, limiting the geometric complexity achievable through resin printing. Contemporary systems employ sophisticated release mechanisms that distribute separation forces more evenly, allowing for the successful printing of thin walls, fine lattice structures, and intricate internal geometries. These mechanisms incorporate precision linear actuators and force feedback systems that monitor and adjust separation parameters in real-time.
The Low Force Display technology represents a significant advancement in reducing the mechanical stresses experienced during layer separation. By minimizing the forces required to detach each layer from the optical window, these systems enable the production of parts with unprecedented detail preservation throughout the build height. The reduced separation forces also contribute to extended hardware longevity, as the mechanical components experience less wear during operation. This technology particularly benefits applications requiring tall, slender features or parts with significant overhangs that would typically require extensive support structures.
Precision Manufacturing Applications and Industry Impact
Medical Device Manufacturing and Biocompatible Production
The medical device industry has embraced advanced stereolithography technologies for producing patient-specific implants, surgical guides, and diagnostic tools with exceptional accuracy. The ability to achieve smooth surface finishes directly from the printer eliminates many post-processing steps traditionally required for biocompatible applications. Advanced display systems enable the production of medical devices with internal channels, complex geometries, and integrated functional elements that would be impossible to manufacture using conventional methods. The precision achievable through these systems ensures proper fit and function for critical medical applications where dimensional accuracy directly impacts patient outcomes.
Biocompatible resin formulations work synergistically with advanced display technologies to produce medical devices that meet stringent regulatory requirements. The consistent light exposure patterns achieved through high-resolution displays ensure uniform material properties throughout the printed part, critical for applications where mechanical performance cannot vary significantly. Quality control processes for medical applications benefit from the predictable results achieved through advanced display systems, enabling manufacturers to establish validated processes that consistently produce parts meeting FDA and CE marking requirements. The reduced need for post-processing also minimizes contamination risks associated with handling sterile or biocompatible components.
Aerospace and Automotive Precision Components
Aerospace applications demand exceptional dimensional accuracy and surface quality for both functional prototypes and end-use components, requirements that align perfectly with advanced stereolithography capabilities. Complex internal cooling channels, lightweight lattice structures, and aerodynamically optimized surfaces can be produced with tolerances approaching traditional machined components. The ability to consolidate multiple assembly components into single printed parts reduces weight while maintaining structural integrity, a critical advantage in aerospace applications where every gram matters. Advanced display systems enable the production of parts with wall thicknesses as low as 0.2mm while maintaining structural integrity throughout complex geometries.
Automotive manufacturers utilize advanced stereolithography for producing functional prototypes, tooling inserts, and low-volume production parts that require precise fitment with existing assemblies. The surface quality achievable through modern systems often eliminates the need for secondary machining operations, reducing production time and costs for complex components. Engine components, transmission parts, and electronic housings benefit from the geometric freedom provided by additive manufacturing while meeting the demanding mechanical and thermal requirements of automotive applications. The consistency of advanced display systems ensures that production parts maintain dimensional stability across temperature cycles and mechanical loading conditions typical in automotive environments.
Technical Specifications and Performance Characteristics
Resolution Capabilities and Layer Height Optimization
Modern stereolithography systems equipped with advanced display technology achieve X-Y resolutions that rival traditional photolithography processes used in semiconductor manufacturing. Pixel sizes as small as 25 micrometers enable the production of features with details visible only under magnification, opening new applications in microfluidics, optical components, and precision mechanical devices. Layer height capabilities extend from ultra-fine 10-micron layers for maximum detail to production-oriented 100-micron layers for faster throughput, providing manufacturers with flexibility to optimize between quality and speed based on application requirements. The relationship between layer height and feature resolution follows predictable patterns that enable process optimization for specific part geometries.
Surface roughness measurements on parts produced with advanced display systems consistently achieve Ra values below 1 micron when optimized processing parameters are employed. This level of surface quality approaches that of injection molding for many polymeric materials, enabling direct use of printed parts in applications where aesthetic appearance matters. The elimination of visible layer lines through optimized exposure patterns and advanced resin formulations reduces or eliminates post-processing requirements for many applications. Dimensional accuracy measurements demonstrate repeatability within ±25 micrometers for features larger than 1mm, providing the consistency required for precision assembly applications.
Material Compatibility and Processing Parameters
The versatility of advanced display systems extends to compatibility with a broad range of photopolymer formulations, from standard resins to specialized materials with unique properties. Engineering-grade resins formulated for mechanical performance, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility can be processed with the same precision as standard materials, expanding the range of functional applications. The uniform light distribution characteristics of advanced displays ensure consistent curing throughout the part volume, critical when working with materials that have narrow processing windows or specific cure requirements. Real-time monitoring systems track exposure energy and adjust parameters automatically to maintain optimal curing conditions throughout the build process.
Processing parameter optimization for advanced display systems involves careful balancing of exposure time, light intensity, and separation forces to achieve optimal part quality while maintaining reasonable production speeds. Automated calibration routines ensure that display brightness and uniformity remain consistent over extended operating periods, maintaining part quality consistency across production runs. The integration of environmental monitoring systems tracks temperature and humidity conditions that can affect resin behavior, automatically adjusting processing parameters to compensate for environmental variations. These systems enable lights-out manufacturing operations where production can continue unattended while maintaining strict quality standards.
Quality Control and Validation Processes
Measurement and Inspection Methodologies
Quality control processes for high-precision stereolithography require sophisticated measurement techniques capable of detecting dimensional variations at the micron level. Coordinate measuring machines equipped with optical probes provide non-contact measurement of complex geometries without risking damage to delicate features. Surface profiling systems quantify roughness characteristics and identify potential defects that could affect part performance in demanding applications. Statistical process control methodologies track dimensional variations over time, enabling proactive adjustments to maintain quality consistency across production batches.
Advanced inspection protocols incorporate both dimensional verification and material property validation to ensure comprehensive part qualification. Mechanical testing of witness coupons printed alongside production parts verifies that material properties meet specification requirements throughout the build volume. Optical inspection systems automated through machine vision algorithms detect surface defects, incomplete features, and other quality issues that manual inspection might miss. Documentation systems maintain complete traceability from raw materials through final inspection, supporting regulatory compliance requirements for industries with strict quality mandates.
Process Validation and Repeatability Studies
Establishing validated processes for high-precision stereolithography involves extensive characterization studies that quantify the relationship between processing parameters and part quality outcomes. Design of experiments methodologies systematically explore the parameter space to identify optimal settings for specific part geometries and material combinations. Capability studies demonstrate that processes consistently produce parts within specified tolerances, providing the statistical foundation required for production qualification. Long-term stability studies track process performance over extended periods, identifying potential drift patterns that require corrective action.
Repeatability validation requires production of statistically significant sample sizes under controlled conditions to demonstrate process consistency. Gauge repeatability and reproducibility studies ensure that measurement systems provide reliable data for process control decisions. Environmental qualification testing verifies that process performance remains stable across the range of temperature and humidity conditions expected in production environments. Change control procedures ensure that any modifications to validated processes undergo appropriate testing and documentation before implementation, maintaining the integrity of qualified manufacturing systems.
Future Developments and Technology Roadmap
Emerging Display Technologies and Performance Enhancement
The evolution of display technology continues to drive improvements in stereolithography performance, with emerging technologies promising even higher resolutions and faster processing speeds. Micro-LED displays offer the potential for significantly increased light intensity while maintaining excellent uniformity across large build areas. Advanced optical systems incorporating adaptive optics could provide real-time correction for optical distortions, ensuring perfect focus across the entire build platform regardless of environmental conditions. Quantum dot enhancement films may enable more precise wavelength control, optimizing photopolymer activation while minimizing unwanted side reactions.
Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into display control systems promises to optimize exposure patterns dynamically based on part geometry and material characteristics. Predictive maintenance algorithms could monitor display performance continuously, scheduling replacement or calibration activities before quality issues occur. Advanced thermal management systems incorporating phase-change materials may enable more consistent operating temperatures, further improving dimensional stability and part quality consistency. The convergence of these technologies suggests that future systems will achieve levels of precision and reliability that approach traditional manufacturing processes while maintaining the geometric freedom inherent in additive manufacturing.
Advanced Materials and Application Expansion
The development of new photopolymer formulations specifically designed for advanced display systems continues to expand the range of functional applications achievable through stereolithography. High-temperature polymers capable of withstanding automotive and aerospace operating conditions while maintaining dimensional stability represent a significant growth area. Conductive and magnetic materials enable the direct printing of electronic components and sensors, potentially revolutionizing how complex systems are manufactured and assembled. Biodegradable formulations for medical applications could enable temporary implants and drug delivery devices with precisely controlled dissolution rates.
Multi-material printing capabilities incorporating different photopolymer formulations within single parts promise to create components with spatially varying properties optimized for specific functional requirements. Gradient materials with properties that change continuously across part geometry could enable new design approaches impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. Smart materials that respond to environmental stimuli could create self-actuating components with embedded functionality. The combination of advanced display systems with these emerging material technologies suggests that stereolithography will continue expanding into new application areas requiring both precision and functionality.
FAQ
What advantages does advanced display technology provide over traditional laser-based stereolithography systems?
Advanced display technology offers several key advantages over laser-based systems, including simultaneous curing of entire layers rather than sequential point-by-point exposure, resulting in significantly faster build times for parts with large cross-sectional areas. The uniform light distribution eliminates the beam quality variations and pointing instability issues common with laser systems, ensuring consistent part quality across the build platform. Lower mechanical complexity reduces maintenance requirements and improves system reliability, while the digital nature of display systems enables precise control over exposure patterns and anti-aliasing algorithms that improve surface quality.
How do Low Force Display systems maintain part quality while reducing separation forces?
Low Force Display systems achieve reduced separation forces through optimized optical window materials and surface treatments that minimize adhesion between cured resin and the display interface. Sophisticated release mechanisms distribute separation forces more evenly across the part cross-section, preventing localized stress concentrations that could damage delicate features. Real-time force monitoring systems adjust separation parameters automatically to maintain optimal conditions throughout the build process. The combination of these technologies enables successful printing of thin walls, fine details, and complex geometries that would fail with traditional high-force separation systems.
What industries benefit most from the precision capabilities of advanced stereolithography systems?
The medical device industry benefits significantly from advanced stereolithography precision for producing patient-specific implants, surgical guides, and diagnostic tools where dimensional accuracy directly impacts patient outcomes. Aerospace and automotive manufacturers utilize these capabilities for functional prototypes, tooling inserts, and end-use components requiring precise fitment with existing assemblies. The electronics industry leverages high-resolution capabilities for microfluidic devices, optical components, and precision mechanical assemblies. Jewelry and consumer products industries benefit from the surface quality and detail resolution for decorative applications requiring minimal post-processing.
What factors should be considered when selecting processing parameters for high-precision applications?
Processing parameter selection requires balancing exposure time, light intensity, and layer height to achieve optimal part quality while maintaining reasonable production speeds. Material characteristics such as absorption depth and cure sensitivity must be considered when establishing exposure parameters for different photopolymer formulations. Environmental conditions including temperature and humidity affect resin behavior and should be controlled or compensated for through parameter adjustments. Part geometry influences optimal layer height selection, with fine features requiring thinner layers while bulk sections can utilize thicker layers for faster production. Support structure requirements and orientation effects on surface quality should also influence parameter selection for specific applications.
Table of Contents
- Revolutionary Display Technology in Modern Stereolithography
- Precision Manufacturing Applications and Industry Impact
- Technical Specifications and Performance Characteristics
- Quality Control and Validation Processes
- Future Developments and Technology Roadmap
-
FAQ
- What advantages does advanced display technology provide over traditional laser-based stereolithography systems?
- How do Low Force Display systems maintain part quality while reducing separation forces?
- What industries benefit most from the precision capabilities of advanced stereolithography systems?
- What factors should be considered when selecting processing parameters for high-precision applications?

