Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a leading - edge industrial 3D printing tech with great perks. It prints without supports, efficiently producing multiple parts in one run, boosting productivity. We offer diverse materials like nylon - based ones and TPU, giving parts heat, chemical resistance, flexibility, and stability. Choose our SLS service for a 3 - working - day standard delivery, getting high - quality prototypes and production - ready parts fast.
| Material properties | Test Standards |
PA12 (1172Pro) |
Test Standards |
PA12+GF30 (1176Pro+GF30) |
Test Standards |
TPU 88A |
| Color | Visual | White | Visual | Grayish black | Visual | Off-white |
| Flexural modulus Mpa | ASTM D790 | 1300 | ISO 178:2019 | 2340 | ||
| Flexural strength Mpa | ASTM D790 | 50 | ISO 178:2020 | 62.6 | ||
| Tensile modulus Mpa | ASTM D638 | 1800 | ISO 527-1:2019 | 2300 | ||
| Tensile strength Mpa | ASTM D638 | 46 | ISO 527-1:2019 | 41.7 | ASTM D638 | 20 |
| Elongation at break | ASTM D638 | 8-15% | ISO 527-1:2012 | 0.068 | ASTM D638 | 350% |
| Heat deflection temperature °C 0.45Mpa | ASTM D648 @66PSI | 179 | ISO 75-1:2013 | 168 | ||
| Heat deflection temperature °C 1.8Mpa | ASTM D648 @66PSI | 99 | ISO 75-1:2020 | 90 | ||
| Density g/cm3 | DIN53466 | 0.95 | ISO 1183-1:2019A | 1.21 | ASTM D1505 | 1.21 |
| Material | Color | Tensile Strength |
Tensile Modulus |
Elongation at break |
Density g/cm3 |
| PA12 (1172Pro) | White | 46Mpa | 1800Mpa | 8-15% | 0.95 g/cm3 |
| PA12+GF30 (1176Pro+GF30) | Grayish black | 41.7Mpa | 2300Mpa | 6.80% | 1.21 g/cm3 |
| TPU 88A | Off-white | 20Mpa | 350% | 1.21 g/cm3 |
|
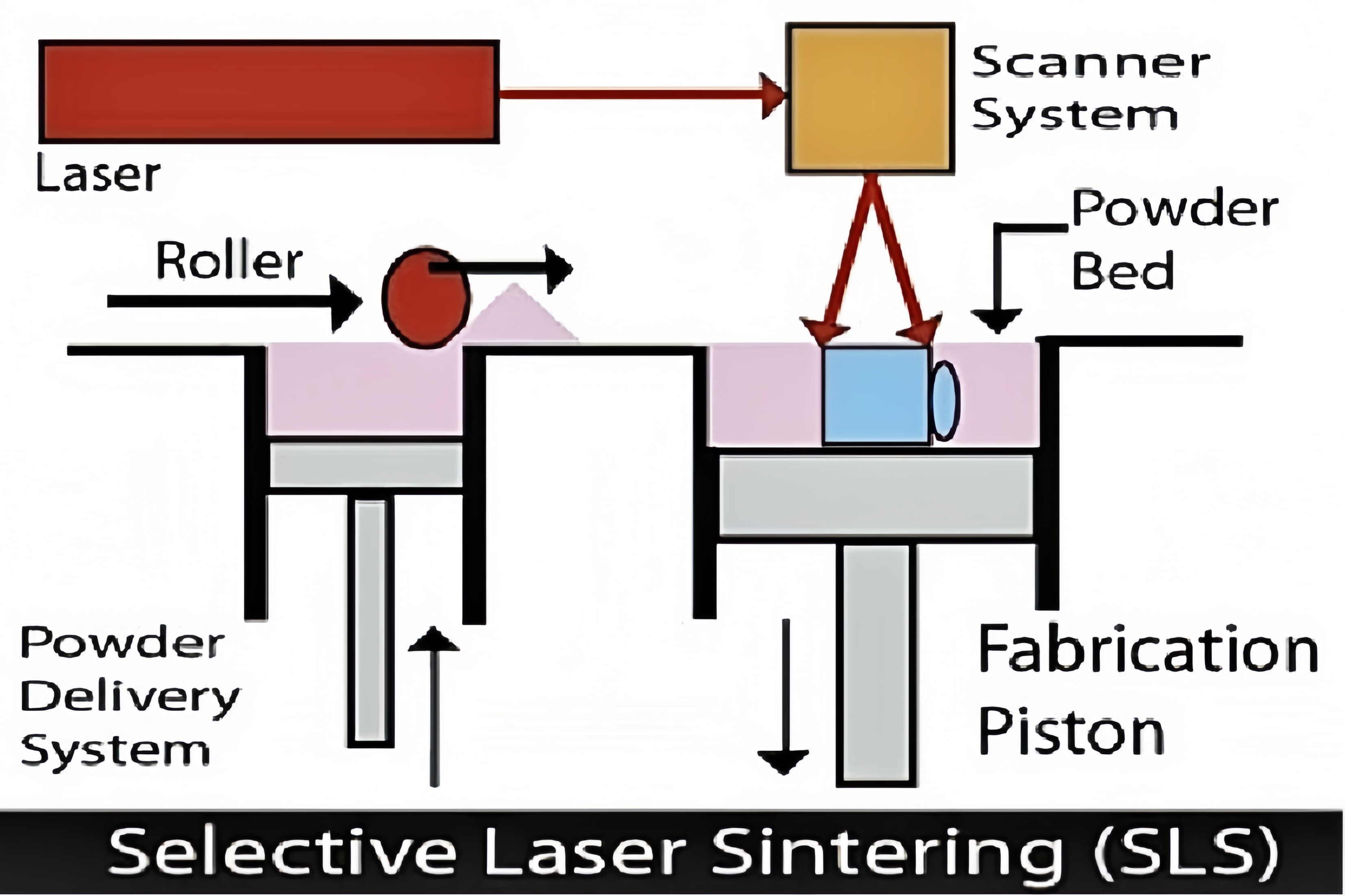
After the SLS 3D printer is initiated, it uses a laser to sinter the material layer by layer onto a heated bed of nylon-based powder according to the geometry of the component. Once a layer of powder has been fused, a roller or a recoater blade moves smoothly across the powder bed to evenly spread the next layer of powder. This process repeats layer by layer until the entire component is printed. After the printing job is completed, the entire powder bed containing the encapsulated components is transferred to the breakout station. At the breakout station, the powder bed is slowly lifted, and then the components are separated and removed from the powder. Next, the staff will carry out an initial manual cleaning to brush off most of the loose powder. Subsequently, the components undergo sandblasting to thoroughly remove any remaining powder residue. After these steps, the components are sent to the post-processing department for subsequent fine finishing. |
 |
|
Advantages
|
Drawbacks
|
